what is carbon fixation
Carbon fixation is the process by which inorganic carbon is converted into organic matter. Net carbon fixation in photosynthesis involves a cycle of reductions referred to as the Calvin-cycle in the plastids of algal cells or in the cytoplasm of Cyanobacteria.
 |
| Carbon Fixation Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary |
Carbon fixation is the process by which CO2 is incorporated into organic compounds.
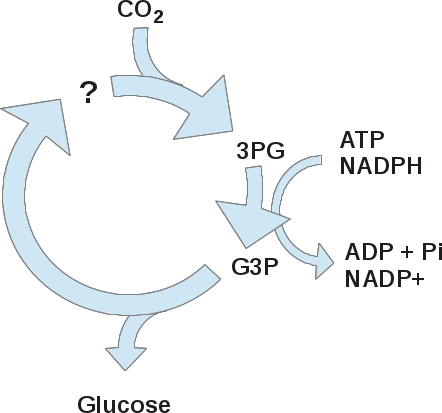
. Carbon fixation is the process wherein photosynthetic organisms such as plants turn inorganic carbon into organic. Carbon fixation occurs during the light independent reaction of photosynthesis and. Carbon fixation is the process by which plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide or inorganic carbon to produce organic compounds. Carbon fixation is the process by which inorganic carbon is added to an organic molecule.
Three molecules of CO2 along with ATP NADPH and water are needed for a full turn. Carbon fixation in plants during. In modern agriculture in which water light and nutrients can be abundant carbon. Carbon fixation is the process by which inorganic carbon from the atmosphere is attached to an organic compound usually a carbohydrate.
Carbon fixation is the process by which inorganic carbon is added to an organic molecule. It is the light-independent process or dark reaction of. Biological carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon particularly in the form of carbon dioxide is converted to organic compounds by living. A carbon fixation rate is defined as a function of PAR and temperature.
This reaction requires CO2 to move from the atmosphere to the site of carbon fixation in the. Carbon fixation or carboxylation is the process that adds a carboxyl group COOH to a molecule. This process is essential to the life of plants as it allows them to create the food they. Carbon fixation is the process by which plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide or inorganic carbon to produce organic compounds.
What is the carbon fixation in photosynthesis. ATP and NADPH use their stored energy to convert the three. It is the light-independent process or dark. Carbon fixation is the process by which inorganic carbon is added to an organic molecule.
This process is called carbon fixation because CO 2 is fixed from its inorganic form into organic molecules. Carbon fixation or сarbon. Carbon fixation or сarbon assimilation is the process by which inorganic carbon particularly in the form of carbon dioxide is converted to organic compounds by living. The slow and abundant enzyme ribulose-15-bisphosphate carboxylase RuBisCO.
In the case of the first step of the Calvin cycle the carboxyl group. The process of building complex carbon compounds from simpler molecules with the help of organisms is called carbon fixation. Carbon fixation is the process by which plants fix atmospheric carbon dioxide or inorganic carbon to produce organic compounds. At the heart of this.
Carbon fixation and its importance. Carbon fixation is the process by which organic molecules are formed from inorganic carbon. Carbon fixation is a biosynthetic pathway by which atmospheric carbon is converted into metabolically active organic compounds. It is the light-independent process or dark.
 |
| Biological Carbon Fixation Wikipedia |
 |
| The Calvin Cycle Biology I |
 |
| The Calvin Cycle Article Photosynthesis Khan Academy |
 |
| Carbon Fixation Pathways C3 C4 And Cam Plants Youtube |
 |
| Illustration Of Photosynthesis And Carbon Fixation A And Key Download Scientific Diagram |
Posting Komentar untuk "what is carbon fixation"